Understanding the Muscles of the Rotator Cuff and Their Functions
Introduction to the Rotator Cuff
The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles and their associated tendons that play a crucial role in shoulder movement and stability. Understanding these muscles is essential for anyone interested in anatomy, sports, or rehabilitation. These muscles work together to allow for a wide range of shoulder motions and to stabilize the shoulder joint.
Each muscle in the rotator cuff has a specific function, and any injury or weakness can lead to significant discomfort and limited shoulder mobility. In this post, we will explore each muscle, its function, and the importance of maintaining rotator cuff health.
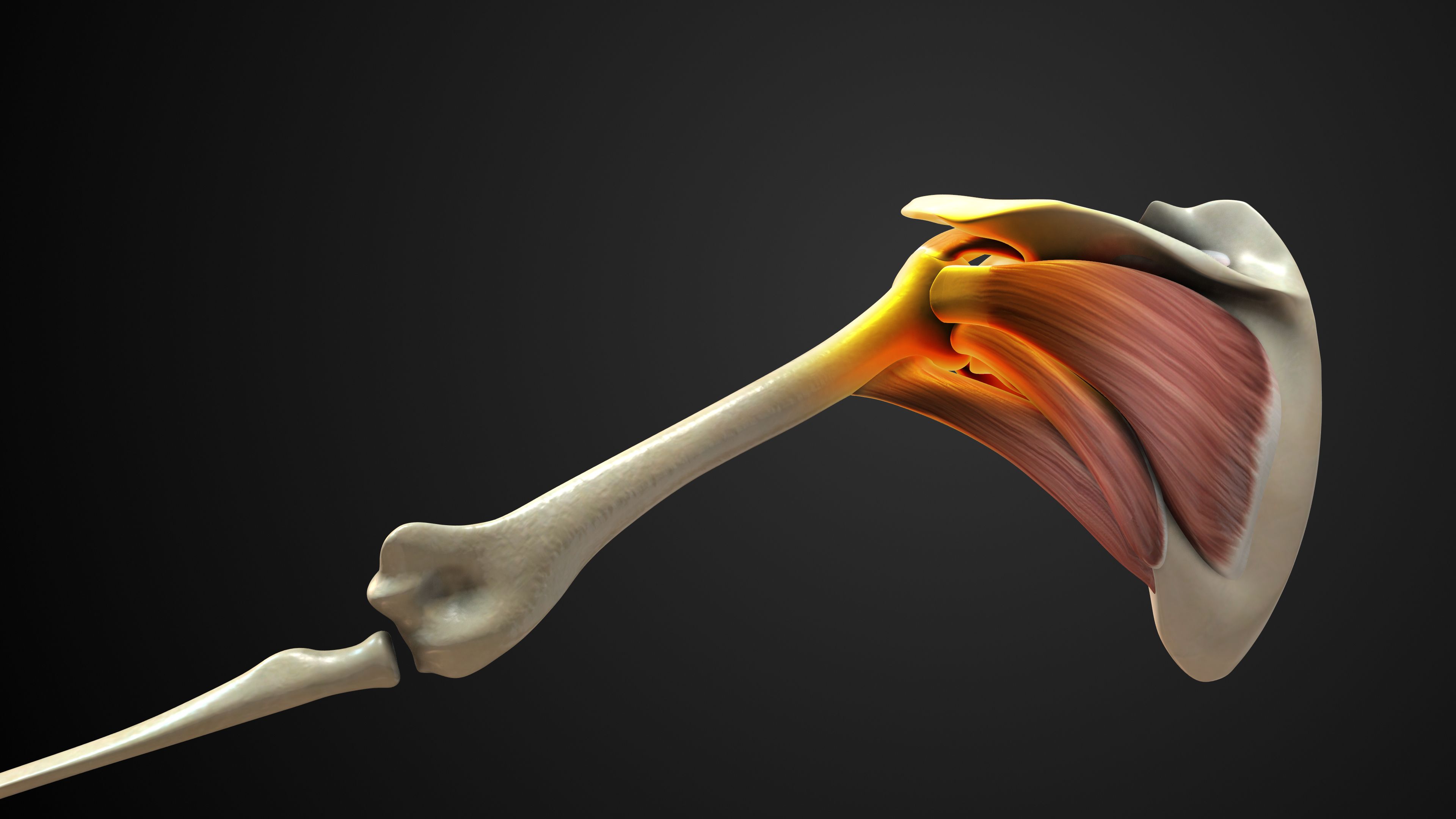
The Supraspinatus Muscle
The supraspinatus muscle is located at the top of the shoulder and is responsible for abducting the arm, or lifting it away from the body. This muscle is often involved in overhead activities and is one of the most commonly injured parts of the rotator cuff.
Strengthening the supraspinatus can help prevent injuries and improve shoulder function. Exercises such as lateral raises and external rotations are effective in targeting this muscle.
The Infraspinatus Muscle
Located below the supraspinatus, the infraspinatus muscle is essential for external rotation of the shoulder. This muscle allows you to rotate your arm outward, a movement crucial for activities such as throwing or swimming.
Weakness or injury in the infraspinatus can lead to instability and difficulty with rotational movements. Strengthening exercises for this muscle include resistance band rotations and reverse flys.

The Teres Minor Muscle
The teres minor is a small muscle located near the infraspinatus. It also aids in the external rotation of the shoulder and works alongside the infraspinatus to stabilize the shoulder joint.
Despite its small size, the teres minor plays a vital role in shoulder health. Incorporating exercises that target this muscle can enhance overall shoulder stability and function.
The Subscapularis Muscle
The subscapularis is the largest muscle of the rotator cuff and is located on the front of the shoulder blade. It is responsible for internal rotation of the shoulder, allowing you to rotate your arm inward.
This muscle is critical for movements such as reaching across the body or behind the back. Strengthening the subscapularis can improve shoulder mobility and reduce the risk of injury.

Maintaining Rotator Cuff Health
Maintaining the health of the rotator cuff muscles is essential for overall shoulder function and preventing injuries. Regular stretching and strengthening exercises can help keep these muscles strong and flexible.
- Incorporate rotator cuff exercises into your routine at least twice a week.
- Focus on proper form to avoid strain and injury.
- Consult with a physical therapist if you experience any pain or discomfort.
Conclusion
Understanding the muscles of the rotator cuff and their functions is crucial for anyone looking to maintain shoulder health and prevent injuries. By focusing on strengthening and stretching these muscles, you can enhance your shoulder stability and performance in various activities.
