Understanding the Muscles of the Hamstrings
Introduction to the Hamstrings
The hamstrings are a group of three muscles located at the back of the thigh. These muscles play a crucial role in various lower body movements, including walking, running, and jumping. Understanding the hamstrings' anatomy is essential for athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and anyone interested in improving their lower body strength.
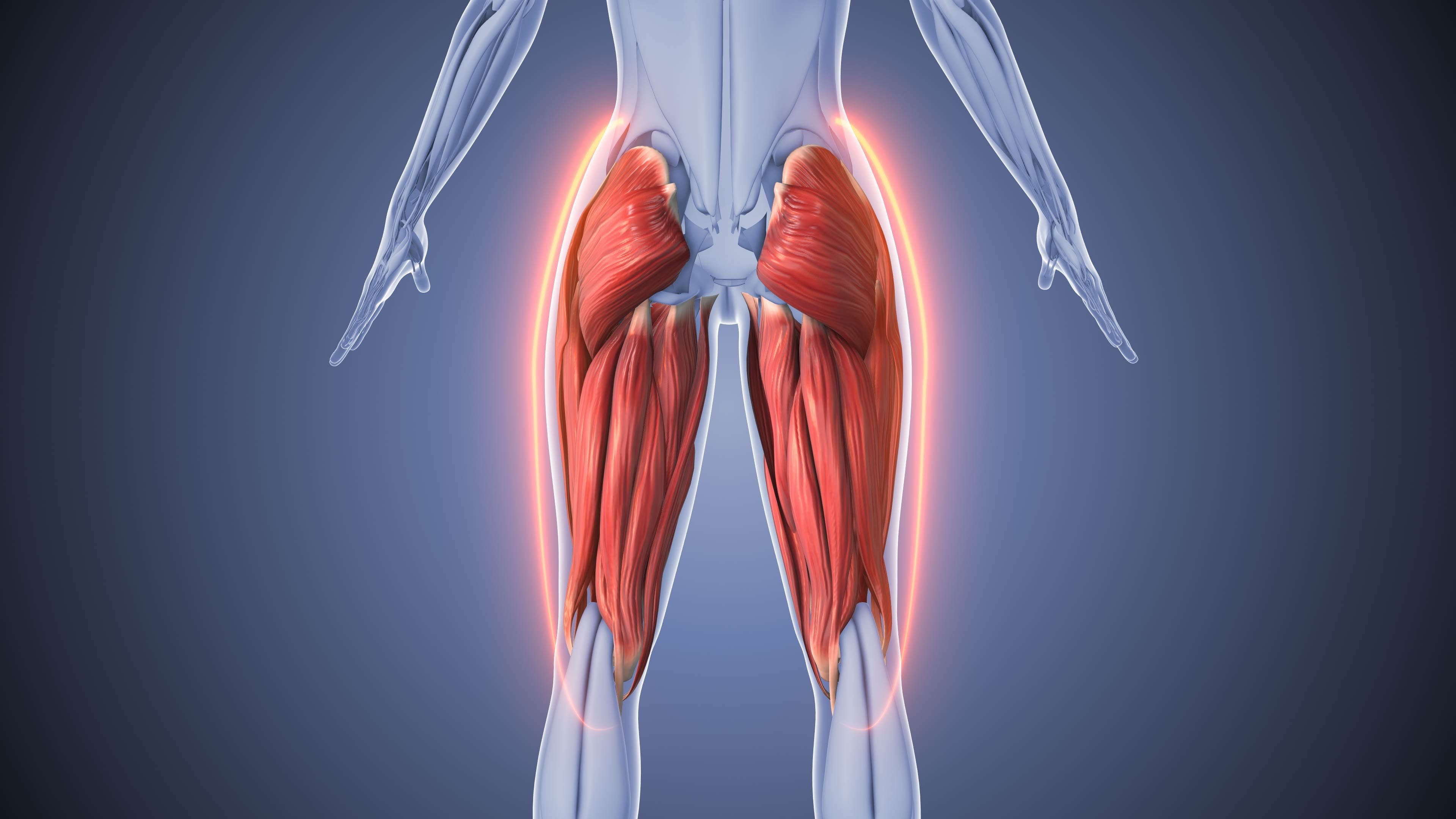
Anatomy of the Hamstrings
The hamstrings consist of three main muscles: the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus. Each of these muscles originates from different points on the pelvis and inserts at various points on the lower leg bones. This configuration allows for complex movements and stability.
Biceps Femoris
The biceps femoris is the most lateral of the hamstring muscles. It has two heads—long and short. The long head originates from the ischial tuberosity, while the short head originates from the femur. This muscle is crucial for knee flexion and hip extension.
Semitendinosus
The semitendinosus lies medially to the biceps femoris. It originates from the ischial tuberosity and inserts into the pes anserinus on the tibia. This muscle aids in knee flexion and internal rotation of the leg.
Semimembranosus
Located beneath the semitendinosus, the semimembranosus also originates from the ischial tuberosity. It extends to the medial condyle of the tibia. This muscle functions similarly to the semitendinosus, facilitating knee flexion and hip extension.
Function and Importance
The primary functions of the hamstrings are to facilitate knee flexion and hip extension. These movements are essential for everyday activities such as walking, sitting, and climbing stairs. Additionally, the hamstrings stabilize the pelvis and contribute to overall posture.

Common Injuries
Hamstring injuries are common, especially among athletes. These can range from mild strains to severe tears. Understanding the hamstrings' anatomy can help in prevention and rehabilitation. Regular stretching and strengthening exercises are key to maintaining healthy hamstrings.
Prevention and Care
To prevent hamstring injuries, incorporate exercises that target flexibility and strength. Warm-up routines and proper stretching before intense activities can significantly reduce injury risk. If an injury occurs, rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) are initial steps to recovery.
Conclusion
Understanding the hamstrings' anatomy and function is vital for optimizing lower body health and performance. By focusing on flexibility, strength, and injury prevention, you can ensure that your hamstrings remain strong and functional throughout your life.
